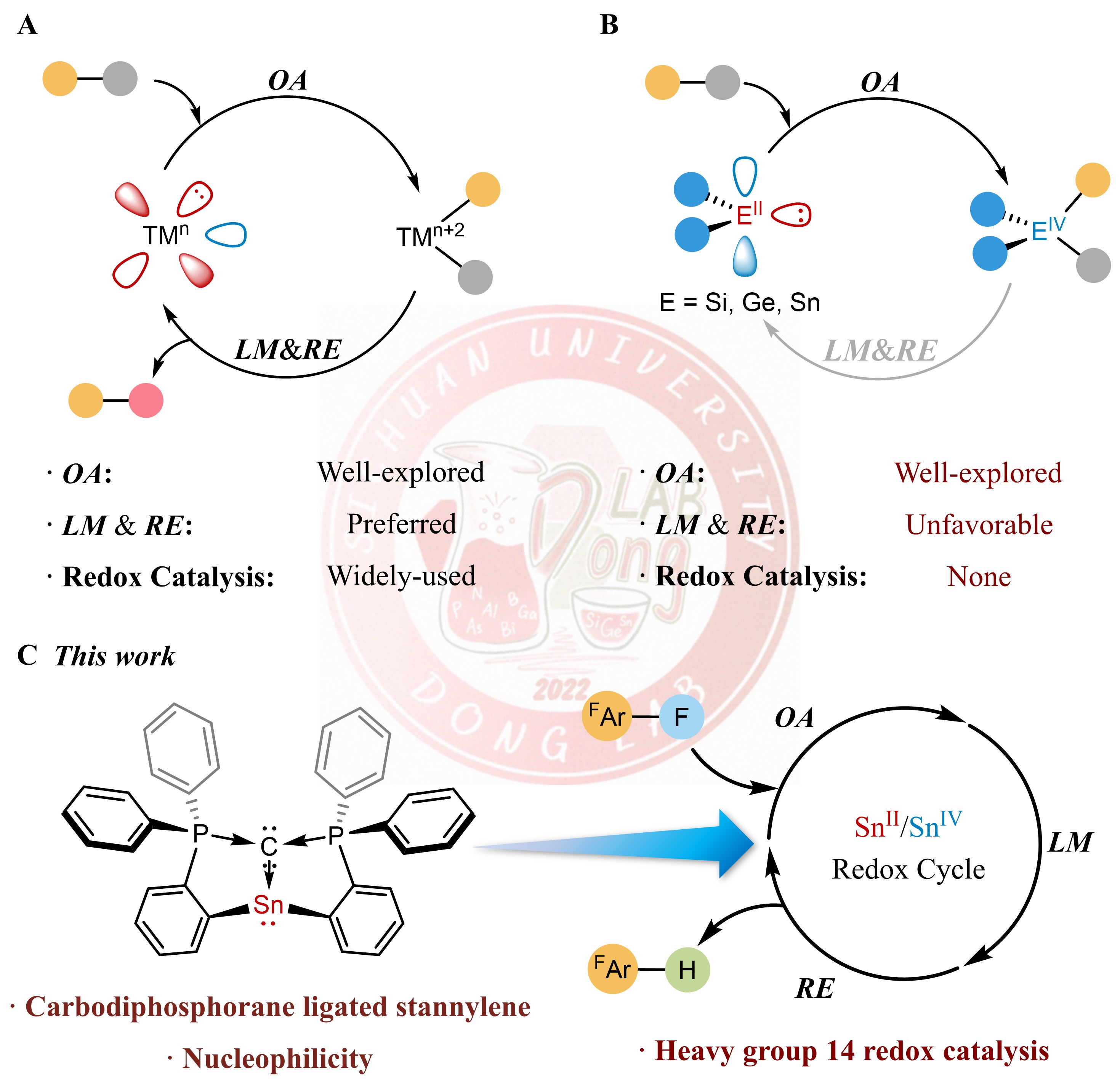
Heavier group 14 carbene analogues, exhibiting transition-metal-like behavior, display remarkable capability for small molecule activation and coordination chemistry. However, their application in redox catalysis remains elusive. In this paper, we report the synthesis and isolation of a stannylene with carbodiphosphorane ligand. The nucleophilic reactivity at the divalent tin center is elucidated by computational and reactivity studies. Moreover, this stannylene exhibits catalytic activity in the hydrodefluorination reaction of fluoroarenes. Mechanistic investigations into the elementary steps confirm a SnII/SnIV redox cycle involving C–F oxidative addition, F/H ligand metathesis, and C–H reductive elimination. This low-valent SnII catalytic system resembles the classical transition metal catalysis. Notably, this represents metallomimetic redox catalysis utilizing carbene analogue with heavier group 14 element as a catalyst.
This study was published in Nature Communications entitled “Synthesis and redox catalysis of Carbodiphosphorane ligated stannylene”. Prof. Zhaowen Dong is the corresponding author of the paper, and Ph.D. student Zhuchunguang Liu and research assistant Zhijun Wang are the co-first authors. This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, National Natural Science Foundation of China, and Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan, China and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Publication link: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-54321-y
