The diamino-substituted aryl cyclobutane backbone is the core structural unit of many drugs or active molecules. Current studies on the C-H bond functionalization of cyclobutane are mainly focused on the C-C bond formation controlled by the guide group, and the metal carbene without the guide group control can only realize the C-H bond insertion reaction at the C-1 or C-3 position of aryl cyclobutane. Compared to C-C bond formation, C-N bond formation of aryl cyclobutane has been less studied. It is challenging to develop a simple and effective synthesis method that can achieve polyamination of aryl cyclobutanes.
To achieve the diamidation of cyclobutane, Yuanhua Wang's group successfully achieved the diamidation of aryl cyclobutane at the C-2,4 position in 30 min with a maximum yield of 86% by using commercially available N-fluorobenzenesulfonimide (NFSI) as the oxidant and non-nitrene nitrogen source through a single-electron oxidation reaction catalyzed by dirhodium catalyst developed in recent years.
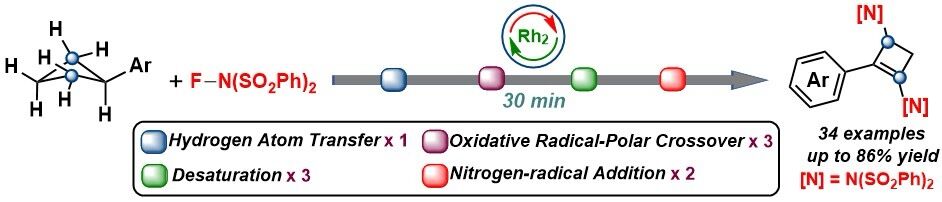
The study of the reaction mechanism confirmed that the reaction did not generate the classical dirhodium nitrene intermediate, but underwent a radical sequential reaction process with nine elementary steps, oxidative radical-polar crossovers, desaturation, and nitrogen-radical addition are the major chemical transformations.
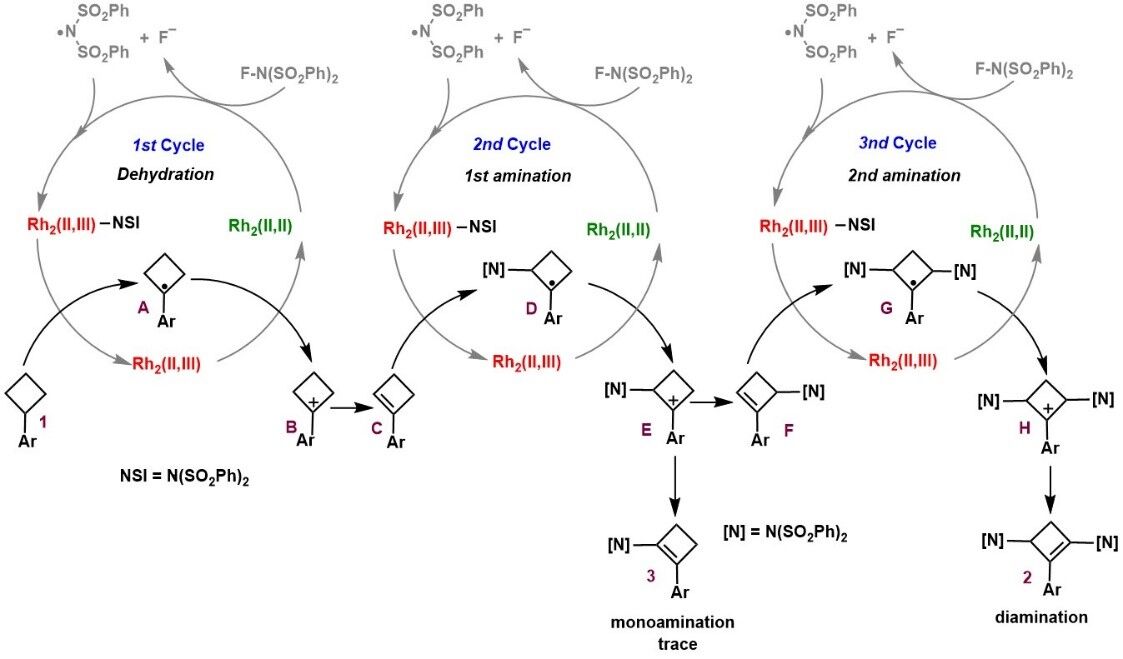
The research results were recently published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition under the title "Rhodium(II)-Catalyzed C(sp3)-H Diamination of Arylcyclobutanes". link: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202205493. We thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China for the financial support.
